
abdominal pain so intense that you can't find a position to relieve it.abdominal pain lasting longer than eight hours.If you think you may be experiencing biliary colic, you should make an appointment with your GP.Ĭontact your GP immediately for advice if you develop: Read more about the complications of gallstones.
SIGNS GALLBLADDER ISSUES SKIN
yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)ĭoctors refer to this more severe condition as 'complicated gallstone disease'.a high temperature of 38C (100.4F) or above.In a small number of people, gallstones can cause more serious problems if they obstruct the flow of bile for longer periods or move into other organs (such as the pancreas or small bowel). When gallstones cause episodes of biliary colic, it is known as 'uncomplicated gallstone disease'.
Some people also have periods where they sweat excessively and feel sick or vomit. After an episode of pain, it may be several weeks or months before you experience another episode. The pain is constant and isn't relieved when you go to the toilet, pass wind or are sick. It's sometimes triggered by eating fatty foods, but may occur at any time of day and it may wake you up during the night.īiliary colic doesn't happen often.

Your liver will still produce bile to digest food, but the bile will just drip continuously into the small intestine, rather than build up in the gallbladder. You can lead a perfectly normal life without a gallbladder. In these cases, keyhole surgery to remove the gallbladder may be recommended. This procedure, known as a laparoscopic cholecystectomy, is relatively simple to perform and has a low risk of complications. complications – such as jaundice or acute pancreatitis.Treatment is usually only necessary if gallstones are causing: 40 or over (the risk increases as you get older).female, particularly if you've had children.You're more at risk of developing gallstones if you're: It's estimated that more than 1 in every 10 adults in the UK has gallstones, although only a minority of people develop symptoms. In most cases the levels of cholesterol in bile become too high and the excess cholesterol forms into stones. Gallstones are thought to develop because of an imbalance in the chemical make-up of bile inside the gallbladder. The gallbladder releases bile into the digestive system when it's needed. The bile is stored in the gallbladder and over time it becomes more concentrated, which makes it better at digesting fats.
SIGNS GALLBLADDER ISSUES SERIES
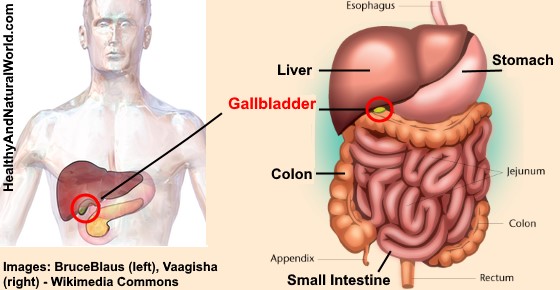
It's passed from the liver through a series of channels, known as bile ducts, into the gallbladder. Its main purpose is to store and concentrate bile.īile is a liquid produced by the liver to help digest fats. The gallbladder is a small, pouch-like organ found underneath the liver. When gallstones cause symptoms or complications, it's known as gallstone disease or cholelithiasis. Some people with gallstones can also develop complications, such as inflammation of the gallbladder ( cholecystitis), which can cause: This type of abdominal pain is known as biliary colic.

However, if a gallstone becomes trapped in a duct (opening) inside the gallbladder it can trigger a sudden intense abdominal pain that usually lasts between 1 and 5 hours. In most cases they don't cause any symptoms and don't need to be treated. Gallstones are small stones, usually made of cholesterol, that form in the gallbladder.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
